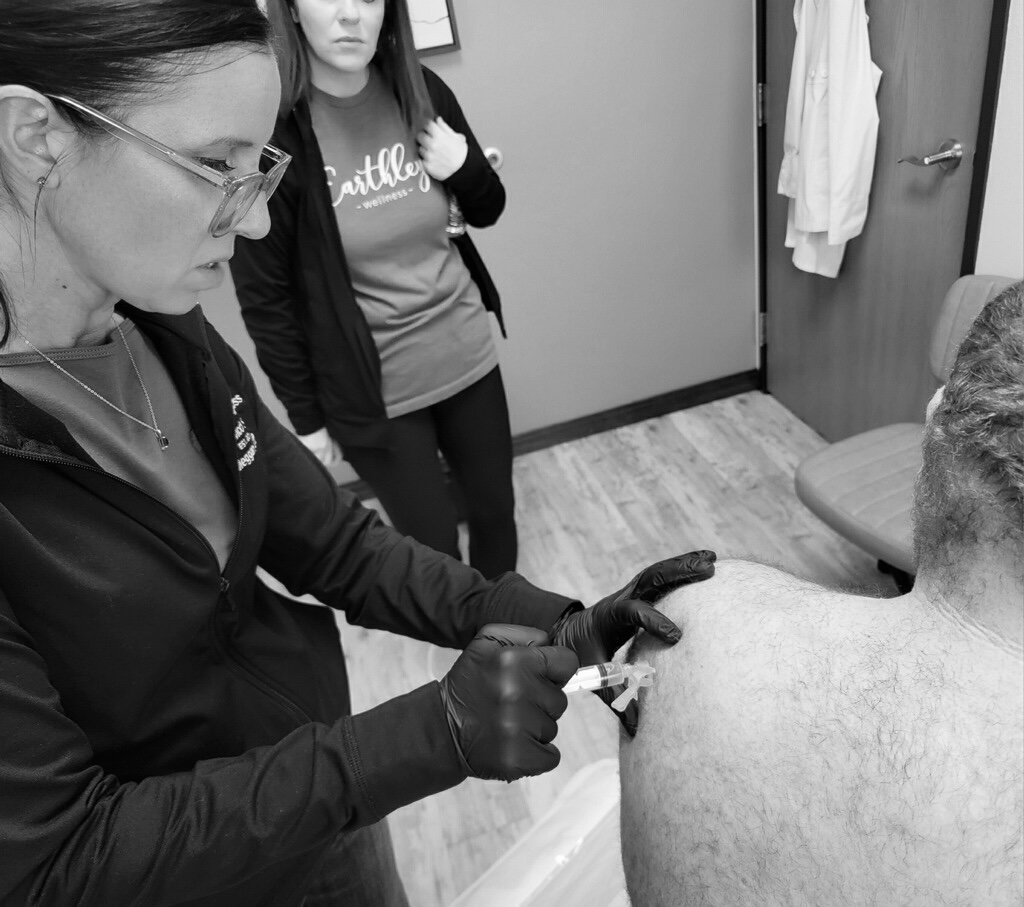
PRP Joint Injections
Joint PRP therapy is an innovative treatment option for individuals experiencing joint pain or degeneration. The growth factors contained within the platelet rich plasma (PRP) stimulate tissue repair and reduce inflammation, leading to improved joint function and reduced pain.
Joint PRP therapy is often considered for conditions such as osteoarthritis, tendonitis, and ligament injuries. Patients may experience a decrease in pain and an increase in mobility, making it an attractive option for those seeking a non-surgical approach to joint health.
-
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is increasingly utilized in the treatment of shoulder injuries and conditions. This injectable treatment is derived from the patient's own blood, which is processed to concentrate the platelets and growth factors.
RESULTS: It is recommended to have PRP treatments done 2 to 3 times, consecutively. Then repeat this once or twice a year for sustained results!
-
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) knee injections are increasingly utilized in the field of orthopedics for various therapeutic purposes. The primary use of PRP injections is to treat knee osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint condition that impacts many individuals, particularly older adults. PRP therapy aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and enhance joint function through the regeneration of damaged tissues.
RESULTS: It is recommended to have PRP treatments done 2 to 3 times, consecutively. Then repeat this once or twice a year for sustained results!
Tell Me More
-
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is obtained through a process that involves several steps:
Blood Collection: A healthcare professional draws a small amount of blood from the patient, generally using a standard blood draw technique. The volume of blood collected typically ranges from 10 to 60 milliliters.
Centrifugation: The collected blood is placed in a centrifuge, which spins at high speeds. This process separates the blood components based on their density. During centrifugation, the blood divides into several layers: plasma, platelets, and red and white blood cells.
Separation of Platelets: After centrifugation, the layer containing the platelet-rich plasma is carefully extracted. This layer typically sits above the red blood cells and below the platelet-poor plasma.
Activation (optional): The obtained PRP can be activated before application, often using substances like calcium chloride or thrombin. Activation triggers the platelets to release growth factors, enhancing their potential therapeutic effects.
Storage or Immediate Use: The PRP will be used immediately for injection into the desired treatment area. We do not store PRP for later use in our office.
Overall, the process is relatively quick and minimally invasive, making PRP a popular choice in various regenerative medicine applications.
-
Here are some common uses of shoulder PRP therapy:
Rotator Cuff Injuries: PRP is often used to enhance healing in rotator cuff tears and tendinopathy, promoting tissue regeneration and reducing pain.
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: By injecting PRP into the affected area, inflammation can be reduced, which may alleviate pain and improve function.
Tendinitis: Conditions like biceps tendinitis and supraspinatus tendinitis can be treated with PRP to encourage healing of the damaged tendon tissues.
Osteoarthritis: PRP may help in managing pain and improving mobility in patients with shoulder osteoarthritis by providing relief from inflammation and stimulating cartilage repair.
Labral Tears: In cases of labral tears, PRP can assist in the healing process, potentially reducing the need for surgery.
Post-Surgical Recovery: Following shoulder surgery, PRP can be used to enhance recovery, decrease swelling, and promote healing of tissues.
Fracture Healing: In certain cases, PRP may support the healing process for fractures in the shoulder by enhancing the body’s natural repair mechanisms.
As with any medical treatment, it's essential for patients to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriateness of PRP therapy for their specific conditions.
-
In addition to osteoarthritis, PRP injections may be beneficial for individuals with acute injuries, such as ligament tears or cartilage damage. The growth factors and proteins in PRP can promote healing by stimulating the repair processes within the joint.
Athletes and active individuals may also turn to PRP injections for conditions such as tendonitis or bursitis in the knee, as this treatment can help speed up recovery and support a return to normal activities.
Overall, PRP knee injections are considered a minimally invasive treatment option that may serve as an alternative to more invasive procedures, such as knee surgery, and can be used in conjunction with physical therapy for optimal outcomes.
-
Consultation:
Before your PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) joint injection, schedule a consultation with your healthcare provider. Discuss your medical history, current medications, and any allergies. This helps determine if PRP is suitable for you.2. Imaging Tests:
Your doctor may recommend imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, to assess the condition of the joint and identify any underlying issues.3. Blood Work:
A blood test might be required to check your platelet levels and ensure proper eligibility for the treatment.4. Medication Review:
Inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you are taking. You may be advised to avoid blood thinners (e.g., aspirin, ibuprofen) for a week prior to the injection, as these can affect platelet function.5. Hydration:
Stay well-hydrated in the days leading up to your injection appointment. Proper hydration supports blood volume and may enhance the quality of the PRP preparation.6. Arrive Prepared:
On the day of the injection, wear comfortable clothing that allows easy access to the treatment area. Arrive with a support person if possible, as you may experience some discomfort post-procedure.7. Post-Injection Care Instructions:
After the injection, your doctor will provide instructions on post-care. This may include rest, avoiding strenuous activity, and managing any pain or swelling.By following these steps, you can better prepare for your PRP joint injection and improve the likelihood of a successful outcome.
-
After receiving a Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) injection in a joint, following proper aftercare is crucial for optimal recovery and effectiveness of the treatment. Here are some recommended aftercare steps:
Rest and Activity Modification: Limit strenuous activities and avoid putting excessive weight on the injected joint for at least 48 hours. Gauge pain levels and adjust activities accordingly.
Ice Application: Apply ice to the injection site for 15-20 minutes every hour as needed for the first 24 to 48 hours. This can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
Pain Management: It's common to experience mild pain or discomfort after the injection. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, can be taken as directed by your healthcare provider. Avoid Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Advil, Aleve, and Naproxen (these are NSAIDS) for 24-48 hours.
Avoid Blood Thinners: Refrain from using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) unless advised otherwise by your physician. These medications may interfere with the healing process.
Hydration: Stay well-hydrated, as this can assist in the healing process and support your overall recovery.
Follow-up Appointments: Attend any scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor progress and ensure proper healing. Your healthcare provider can offer personalized advice based on your individual recovery.
Physical Therapy: If recommended, engage in physical therapy to enhance joint function and promote healing. Follow your therapist's instructions carefully regarding exercises and activities.
Observation of Symptoms: Monitor the injection site for any signs of infection, such as increased swelling, redness, warmth, or discharge. If you experience unusual pain or persistent symptoms, contact your healthcare provider.
Gradual Return to Activity: After the initial rest period, gradually increase activity levels as tolerated. Listen to your body and avoid pushing past discomfort.
By adhering to these aftercare guidelines, you can support the healing process and enhance the benefits of your PRP injection. Always consult with your healthcare provider for specific instructions tailored to your situation.